Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are commonly associated with women, but men are also susceptible to these painful and disruptive infections. Though less frequent, UTIs in men can be serious and often signal underlying health issues that require medical attention. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures for UTIs in men, helping you stay informed about your urological health. If you’re experiencing symptoms or need expert care, Mohandai Oswal Hospital in Ludhiana provides specialized urology treatment to ensure optimal urinary health.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
A UTI is an infection in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. In men, these infections usually affect the lower urinary tract, comprising the bladder and urethra. If left untreated, a UTI can spread to the kidneys, causing severe complications.
Causes of UTIs in Men
Several factors contribute to UTIs in men. Understanding the causes can help in early diagnosis and prevention.
- 1. Bacterial Infections
Most UTIs result from bacteria, particularly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally reside in the intestines but can invade the urinary tract. - 2. Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - BPH)
As men age, the prostate gland can enlarge, blocking urine flow and creating a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to frequent infections. - 3. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones obstruct the urinary tract, making it easier for bacteria to multiply and cause infections. - 4. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Certain STIs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can lead to UTIs by infecting the urethra. - 5. Diabetes and Weakened Immune System
Diabetes and conditions that weaken the immune system can make men more susceptible to infections, including UTIs. - 6. Catheter Use
Men who require urinary catheters due to surgery, injury, or chronic conditions are at a higher risk of developing UTIs. - 7. Poor Hygiene
Not maintaining proper genital hygiene can increase bacterial growth, leading to infections. - 8. Unprotected Sexual Activity
Unprotected intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, leading to infections.
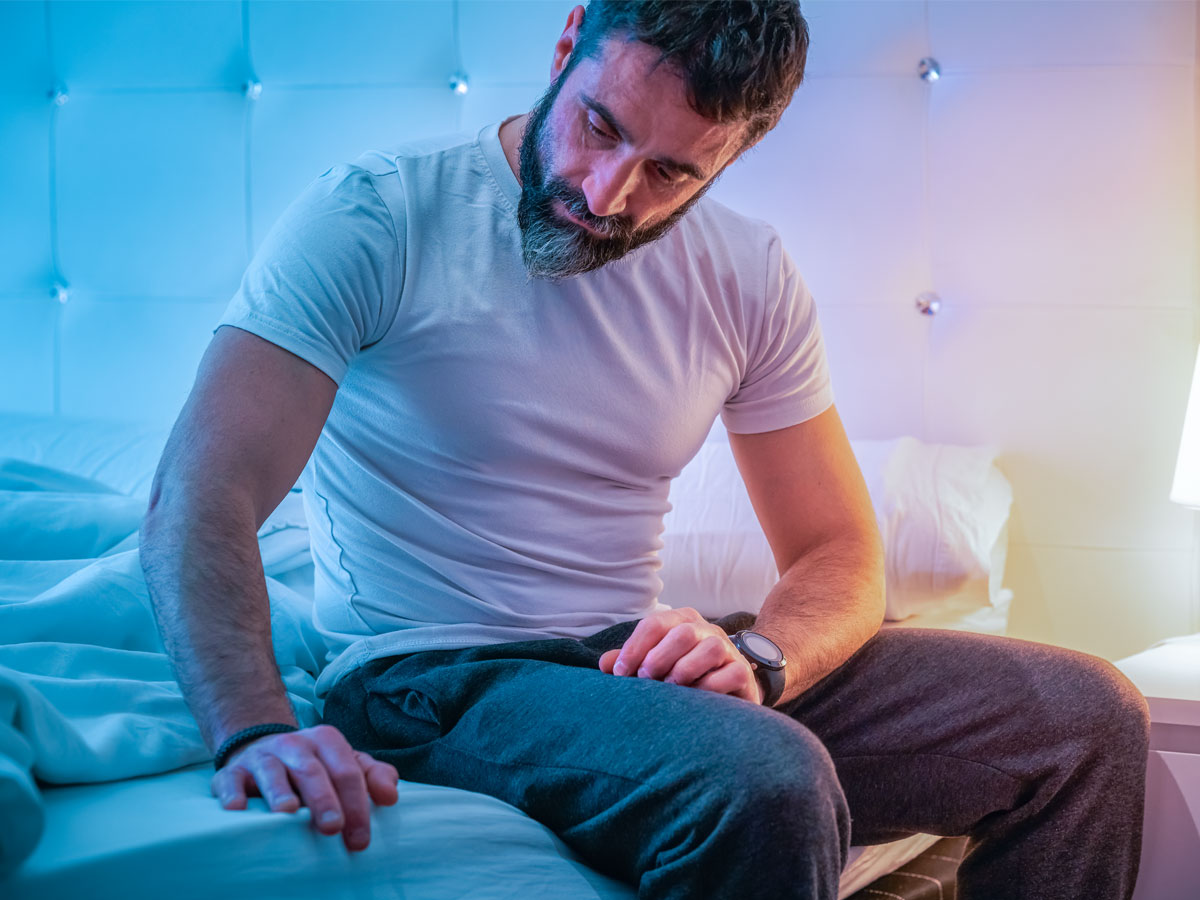
Symptoms of UTIs in Men
Recognizing UTI symptoms early can prevent complications. Common symptoms include:
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urination with little output
- Strong urge to urinate, especially at night
- Cloudy, dark, or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Pain in the lower back or sides, which could indicate a kidney infection
- Fever, chills, and fatigue (in severe cases)
If you experience these symptoms, consult a urology specialist at Mohandai Oswal Hospital in Ludhiana for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing UTIs in Men
Doctors use several diagnostic tests to confirm a UTI:
- 1. Urinalysis
A urine sample is examined for bacteria, white blood cells, and red blood cells. - 2. Urine Culture
This test identifies the specific bacteria causing the infection and helps determine the best antibiotic treatment. - 3. Ultrasound or CT Scan
Imaging tests help detect kidney stones, blockages, or other abnormalities that may contribute to recurrent infections. - 4. Cystoscopy
A thin tube with a camera is inserted into the urethra to examine the bladder and urinary tract.